email: info(at)go-eu.com
phone: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60



assisted in a company setup.

Below we cover all types of taxes in Romania and note what has changed
in 2026 and which tax rates apply. Before we start and examine all Romanian taxes,
we would like to discuss the differences in tax revenues within the EU. The
differences within the countries are serious.
We clarify:
How much tax do you pay in Romania?
(for example DE vs. RO) - how much is left?
Here are Germany's, a Western European country, revenues measured by GDP. Simply put, Germany generated 46.7% of revenue measured by the annual gross domestic product in 2019. The German state coffers were therefore filled with almost 50% of the total GDP.
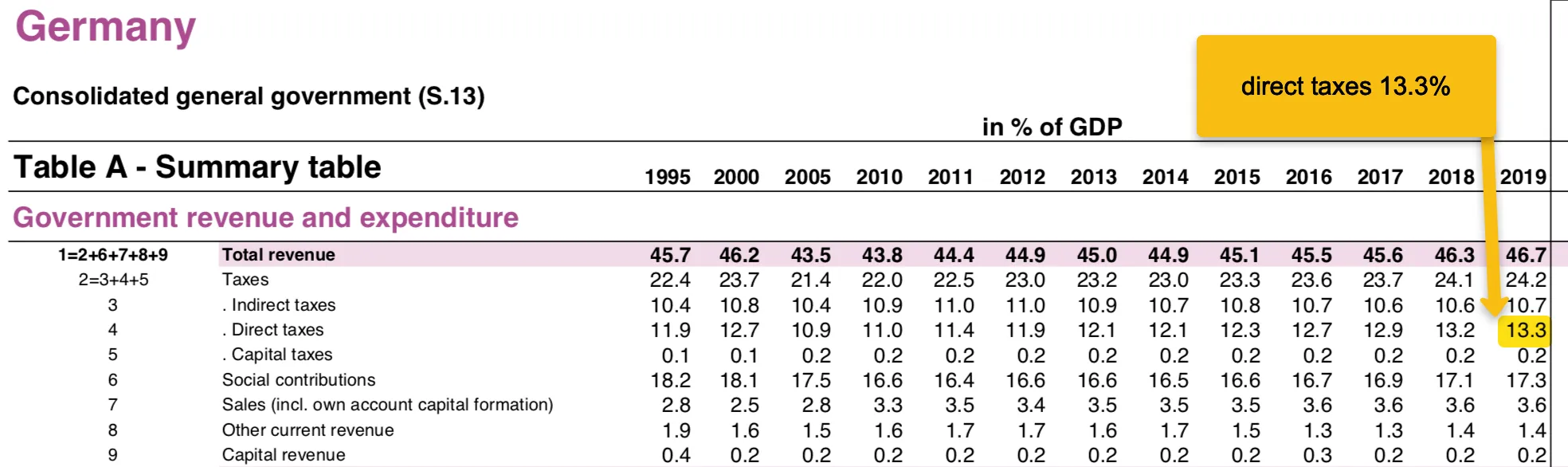 Source: ec.europa.eu
Source: ec.europa.eu The influence of politics in Germany and its strict tax policy with hidden and also openly
visible tax increases accurately reflect the steadily increasing percentage of revenues.
Starting from 43.8% in 2010 to over 46.7% in 2019.
One of the highest values in the EU: 13.3% direct tax revenue*/GDP 2019
In addition, we provide further legal advice in this article
to help you save taxes as best as possible.
Here are the revenues of Romania measured by GDP. Simply put, Romania generated 31.8% of revenues measured by the annual gross domestic product in 2019.
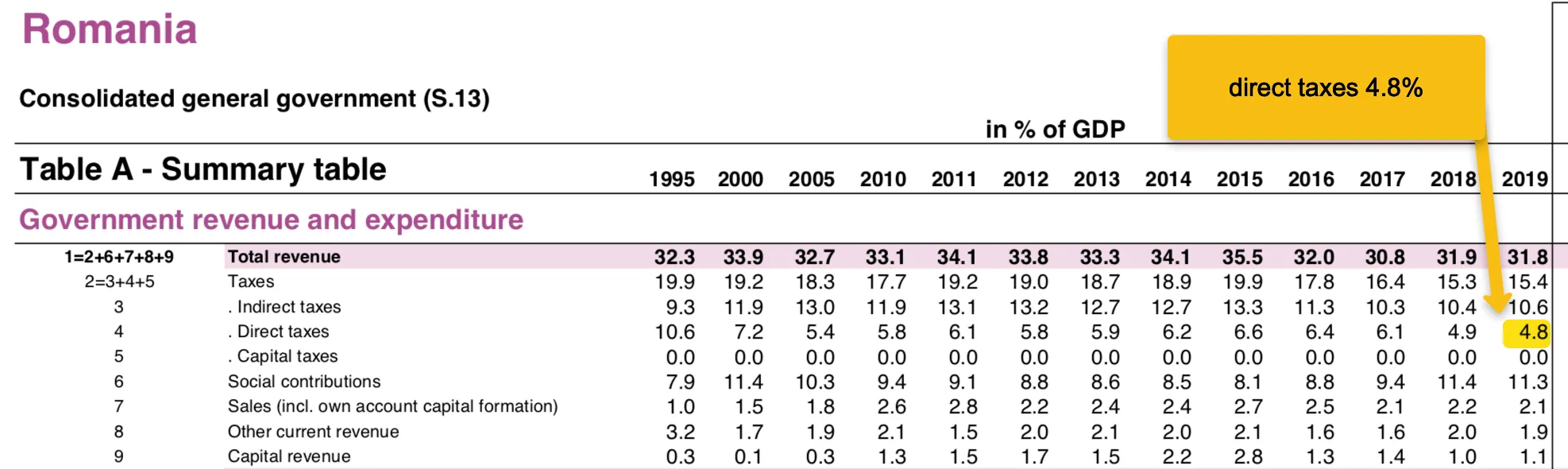 Source: ec.europa.eu
Source: ec.europa.eu The tax policy in Romania reduces taxes year after year to stimulate investment and
immigration. Starting from 1995 with 10.6% direct taxes/GDP to 4.8% in 2019.
Lowest value in the EU: 4.8% direct tax revenue*/GDP 2019
*Direct tax revenues: corporate tax, income tax, etc.
Here is an overview of the Romanian taxes:
1. Corporate Tax Romania (SRL)
2. Capital Gains Tax Romania Dividends
3. Profit Tax Romania
4. VAT Romania
5. Income tax Romania
6. Payroll tax Romania
7. Tax Consulting Romania Accounting
8. Company foundation Romania
We answer all your questions about a company setup Romania – free of charge and without obligation.
Inquire now
Over 500 successful foundings. Answer in 24h.
Or give us a call: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60
(NEW: Company formation including bank account opening 100% remote)
1. Corporate tax for capital companies
We answer all your questions about a company setup Romania – free of charge and without obligation.
Inquire now
Over 500 successful foundings. Answer in 24h.
Or give us a call: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60
(NEW: Company formation including bank account opening 100% remote)
The corporate tax, also known as a company tax, is calculated as a percentage
of the profit or turnover of a company. First of all, it should be mentioned that
there is no trade tax in Romania. The valid tax rate at company level for
capital companies is 16% of the profit. A capital company or legal entity in
Romania, like the Limited Liability Company, is equivalent to the Romanian legal
form of the S.R.L.

There is a special case in Romania: In Germany, for example, limited liability companies or general companies are considered basic company structures and are taxed at the personal income tax rate.
It is different in Romania: The two legal forms S.C.S. (limited partnership) and S.N.C. (general partnership) are also legally regarded as capital companies in Romania and are subject to this taxation.
However, there is a notable exception to the
corporate tax of 16% on profits:
1. If the company's turnover falls below 100,000 EURO per year
a) The company can become a profit tax payer company, which results in paying 16% tax on the profit
b) Or only pay 1-3% tax up to 100,000 EURO on annual turnover
Example: The company "Baumann" has a turnover of €100,000 in 2026 and generates a profit of €100,000
Question: What taxes will be due?
Answer: If you have at least one employee, you have to pay a tax of 3% on your turnover of €100,000.
You have to pay €3,000 in taxes - and that's with a profit of €100,000! (If you have no employees, it's 16% = €16,000 in taxes)
Mistake 1: If the corporate profit tax rate in Romania is 16%, €16,000 in taxes would have to be paid.
Mistake 2: If the corporate profit tax rate in western countries on average is 30%, €30,000 in taxes would have to be paid.
This only applies to corporate taxation - are profit distributions planned - DE and RO differ drastically again!
➼ Further information:
➔ Contact us: Inquire now➔ Company Romania: Company formation Romania in 5 steps
➔ Reseidence in Romania: Work permit Romania
➔ Business Romania: Business in Romania as a foreigner
We answer all your questions about a company setup Romania – free of charge and without obligation.
Inquire now
Over 500 successful foundings. Answer in 24h.
Or give us a call: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60
(NEW: Company formation including bank account opening 100% remote)
2. Capital Gains Tax / Dividend Tax in Romania
We answer all your questions about a company setup Romania – free of charge and without obligation.
Inquire now
Over 500 successful foundings. Answer in 24h.
Or give us a call: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60
(NEW: Company formation including bank account opening 100% remote)
The capital gains tax, also known as withholding tax, is calculated as a
percentage of the profit to be paid out. Whether profits are distributed
in the form of a dividend from your own company or dividend payments from
listed companies (shares) held, a dividend tax is payable. In Romania this is 16%.

Investments by Romanian companies in other Romanian companies and the payment of dividends
between them do not trigger dividend tax and are completely tax-free. The condition that a
stake of at least 10% has existed for at least 1 year has been removed. Dividends that a foreign
company receives as a result of an investment in a Romanian company are taxed at 16% at source.
Parent-subsidiary companies in Romania can therefore shift profits tax-free.
A profit distribution for natural persons triggers 16% dividend tax:
1. If the distribution falls below 48,600 RON (approx. 9,900€) per year:
a) There is no additional social security tax in Romania
b) If the limit is exceeded, natural persons residing in Romania will be charged 4,050 RON (approx. 800 EUR). Never more!
c) If the limit is exceeded, natural persons who do not reside in Romania will no longer have to pay any additional social security tax in Romania!
d) If the limit is exceeded, legal entities, regardless of where they are located, will no longer be required to pay any additional social security tax in Romania.
Example: The company "Erdmann" has a turnover of €100,000 in 2026 and generates a profit of €100,000.
€100,000 in profit is now to be paid out to the managing director as a dividend.
Question: What taxes are due on the distribution of profits?
Answer: €100,000 is to be paid out, which means that 16% dividend tax is due.
The managing director, Mr Erdmann, lives in a country with low taxes (for example the UK or
Cyprus) and has his profits paid out there. Only 3% tax is due on €3,000. A dividend tax of
16% is not due due to the EU parent-subsidiary directive and his place of residence - and there
are also no social security contributions. He has €97,000 of the €100,000 original company
profit left to use as he pleases.
Mistake 1: Don't pay out profits too quickly. A company should mature
for 1-3 years before paying out to individuals. Better: make real estate or other
investments.
Mistake 2: Simply transfer profits (withdrawals) to your own private account in your home country.
If you invest in a Romanian property instead of a profit payout and have the rental income transferred to your private account in your home country - this income is exempt from tax. (Clearly regulated in the DBA)
For comparison: In Germany, 26.75% tax is levied on profit distributions.
3. Profit tax in Romania
A profit tax is, as the name suggests, a tax on profit. As discussed above,
a profit tax of 16% is due for capital companies - or if you choose a micro-company
with a turnover of up to EUR 100,000 per year - then the tax on turnover is 1-3%.
Profit withdrawals (dividends) are taxed at 16%. For further details,
please contact 1. Corporate tax
and 2. capital gains tax / dividends to take a closer look.

Romania is bravely continuing to reduce all profit taxes year after year. Since 2018,
income taxes for individuals have been reduced from 16% to 10%. The turnover level for
capital companies has been increased from €100,000 to €250,000 in 2025 in order to benefit
from the 1-3% tax rate. in 2026 it is €100,00 threshold. Dividend payments to private individuals were still subject to a
15% tax burden in 2015. Since 2026, a uniform 16% dividend tax has applied.
In order to prevent emigration and promote immigration, further tax relief is expected in the coming years.
We answer all your questions about a company setup Romania – free of charge and without obligation.
Inquire now
Over 500 successful foundings. Answer in 24h.
Or give us a call: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60
(NEW: Company formation including bank account opening 100% remote)
We answer all your questions about a company setup Romania – free of charge and without obligation.
Inquire now
Over 500 successful foundings. Answer in 24h.
Or give us a call: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60
(NEW: Company formation including bank account opening 100% remote)
4. VAT Romania
VAT liability, which means an obligation to apply for a VAT ID and to register for VAT,
is binding for sales of more than 300,000 RON per year. Depending on the exchange rate,
this is around 60,000 EUR. Natural and legal persons who make more than the equivalent
of around 60,000 EUR in sales per year are obliged to declare and pay VAT. The standard VAT rate is 19% in Romania.

When Romania joined the EU, it also adopted the so-called reverse charge procedure.
If the reverse charge regulation is used, the invoice is issued without VAT. This
regulation applies to corporate customers who also have a VAT ID. In the books of
the supplier and customer as well as in the VAT returns, the VAT (which has not actually
been paid) is recorded both as deductible and as collected VAT.
Exports to third countries are exempt from VAT
1. A reduced VAT rate or exemption from VAT shall only apply in these cases
a) Exemptions apply to: social, medical institutions, education and research
b) Exemptions apply to: investment firms, credit and insurance businesses
c) 9% VAT on medicines, food and hotels
d) 5% VAT for culture, cinema and magazines
Example: The entrepreneur "Rudermann" makes a turnover of €100,000 in 2026
with digital goods and therefore has no expenses (profit: €100,000). The turnover is 50%
each from private and corporate customers within the EU.
Question: Which sales taxes are due?
Answer: Mr. Rudermann is subject to sales tax and does not pay sales tax on
50% of his sales thanks to the reverse charge procedure. He owns a second Romanian company
that his private customers pay their invoices to. The second company has a turnover (50k)
of less than €60,000 and is therefore a small business and exempt from sales tax.
Mistake 1: No splitting up in several companies to save VAT.
Mistake 2: No use of the reverse charge procedure
Up to three companies per person may be operated with a 60k EUR threshold to be exempt from VAT. Generally 3 companies at the same time per person.
5. Income tax Romania
In general, a flat income tax rate of 10% applies to private persons.
This only has to be paid by self-employed persons and freelancers who live in
Romania and have chosen a sole proprietorship (SA) rather than a corporation. Romania,
including Bulgaria, has the lowest income tax rate in the EU at 10%. However, there are
exceptions for even lower tax rates: (e.g. tax rate for income from the transfer of
real estate, etc.)

Exemption from income tax: The Romanian state has classified a few categories of employees
as exempt from income tax. Among them: IT specialists – To obtain the tax exemption, a well-documented
process must be followed under strict regulations.
A profit distribution (e.g. from a sole proprietorship) can trigger a small additional tax for natural persons:
1. If the distribution is less than 48,600 RON (approx. 9,900€) per year:
a) There is no longer any extra tax for private persons in Romania.
b) If the limit is exceeded, natural persons residing in Romania will have to pay an additional social security tax of RON 4,050.
c) If the limit is exceeded, private persons who are not resident in Romania and regardless of where they live will no longer have to pay any additional social security tax in Romania.
d) For corporations, regardless of where they are located, no additional social security tax is payable in Romania.
Example: The company "Wassermann" has a turnover of €100,000 in 2026 and generates a profit of €100,000.
€100,000 in profit is now to be paid out to the managing director as a dividend.
Question: What taxes are due on the payout of winnings?
Answer: €100,000 is to be distributed, which means that 16% dividend tax is due.
The managing director, Mr Wassermann, lives in a low-tax country and has his profits paid out there.
He has €84,000 left over for his own use.
Mistake 1: Don't pay out profits too quickly. A company should mature for 1-3
years before paying out to individuals. Better: make real estate or other investments.
Mistake 2: Simply transfer profits (withdrawals) to your own private account in your home country.
If you invest in a Romanian property instead of a profit payout and have the rental income transferred to your private account in your home country - these earnings are exempt from tax. (Clearly regulated in the European DBA)
For comparison: In Germany for example, 26.75% tax is levied on profit distributions.
➼ Further information:
➔ Contact us: Inquire now➔ Company Romania: Company formation Romania in 5 steps
➔ Reseidence in Romania: Work permit Romania
➔ Business Romania: Business in Romania as a foreigner
6. Payroll tax Romania
The income tax for salaries and wages is 10%. Social security contributions and income tax
are calculated, withheld and paid by the employer. The total employee share is: 45%. The
total employer share is: 2.25%

25% pension insurance employee share, of which 3.75% is for private pension provision
4-8% Pension insurance for special employment conditions Employer's contribution
10%
health insurance contribution of the employee's monthly gross income.
2.25% unemployment
insurance contribution of the employer's monthly gross income.
4050 RON gross = 2450 RON net (employee share 45% = 25% pension insurance, 10% health insurance, 10% income tax)
7. Tax advice in Romania
Over many years in Romania, we have created a network of experts with the best tax
consultants and accountants. Their expertise goes beyond ordinary bookkeeping
and accounting. They have knowledge of tax regulations at national and international
level.

- Tax Consulting in Romania
- Tax advice related to various double taxation agreements
- Many years of knowledge in international and national tax law
- Development of tax strategies instead of standardized accounting
- Direct contact for any tax questions
- No rotation of different employees
From experience: Choose an expert tax advisor rather than a large tax office - where costs are higher and you are just a number. We can help you. Just talk to us!
We answer all your questions about a company setup Romania – free of charge and without obligation.
Inquire now
Over 500 successful foundings. Answer in 24h.
Or give us a call: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60
(NEW: Company formation including bank account opening 100% remote)
We answer all your questions about a company setup Romania – free of charge and without obligation.
Inquire now
Over 500 successful foundings. Answer in 24h.
Or give us a call: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60
(NEW: Company formation including bank account opening 100% remote)
8. Company setup in Romania
Setting up a company in Romania is particularly worthwhile for medium-sized companies.
Taxes are levied on sales of up to EUR 250,000 per year - and only at 1-3%. Romania
has one of the most liberal small business regulations in the EU. The upper limit is
around EUR 60,000 per year, in other European countries the average is 22,000 - 30,000 to be exempt from sales tax. Make
just under EUR 5,000 per month in sales and do so without paying sales tax. Several small
companies can be set up quite legally in order to save further sales tax.

- Lowest taxes in the entire EU
- Avoiding double taxation through the double taxation agreements
- Low-wage sector with well-trained personnel in certain areas (e.g. IT)
- Managing directors and shareholders are not publicly named (anonymous)
- Direct contact for any tax questions
- Recognition of the EU company by the domestic tax office
You want to start a company in Romania? Request advice or call us directly! Our expertise specializing in Romania, including our network of experts, will help you in almost all matters.
➼ Further information:
➔ Contact us: Inquire now➔ Company Romania: Company formation Romania in 5 steps
➔ Latest Taxes in Romania: Tax Rates 2026
➔ Reseidence in Romania: Work permit Romania
➔ Business Romania: Business in Romania as a foreigner
We answer all your questions about a company setup Romania – free of charge and without obligation.
Inquire now
Over 500 successful foundings. Answer in 24h.
Or give us a call: +49 (0)89 90 42 23 60
(NEW: Company formation including bank account opening 100% remote)

Ralf Kneissler
Published on 27 September, 2021 / Answer
This is exactly what I was looking for! Very detailed and understandable.
Jonas
Published on 27 September, 2021 / Answer
60,000 euros/year VAT-free. Almost 5k a month. You write that multiple small businesses can be founded, meaning each company would then be VAT-exempt by 60k, right?
Kareem
Published on February 14, 2022 / Answer
The 10% income tax only applies to individuals residing in Romania? Have I understood that correctly?
Thomas Hofmann
Published on February 14, 2022 / Answer
Exactly! For individuals who are not resident in Romania or live in Germany, Austria, or Switzerland, the 10% income tax is not payable – because operating a Romanian corporation (SRL) is only subject to a capital gains tax of 1% (up to 250.000 EUR in annual revenue), as well as an 10% dividend tax on profit withdrawals.
Theo L.
Published on 01 November, 2022 / Answer
A few percent in taxes is nothing. Should it really stay this way? Will the EU go along with it in the long term?
Thomas Hofmann
Published on 02 January, 2022 / Answer
Hello Theo, thank you for your message. Romania continues to have a huge problem with the brain drain and low influx of companies and investments. Yet economic growth is among the highest in the EU. Tax rates are the lowest in the EU—and that's true—and they're expected to stay that way for some time to come. Since 2018, we've even been able to count on ever-increasing tax breaks. Before 2018, the 1% tax only applied to income up to €100,000 per year. In 2022, annual revenue of 250.000 EUR and one employee will be required to qualify for 1% tax.
Taxfreund
Published on 12 September, 2024 / Answer
Germany has completely let me and many others down. Romania, I am open for you!
Taxfreund
Published on 12 September, 2024 / Answer
Deutschland hat mich komplett und viel Anderen komplett im Stich gelassen. Romania I am open for you!
Heffner Max
Published on 13 January, 2025 / Answer
Only you have the most up-to-date information on taxes for 2025. Thanks!
Sofia
Published on 22 March, 2025 / Answer
The difference in tax burden between Romania and Germany is huge!!
Rebecca Stanciu
Published on 07 December, 2025 / Answer
Go Romania! I love my country
Leave a comment